What is Porosity in Welding: Important Tips for Achieving Flawless Welds
What is Porosity in Welding: Important Tips for Achieving Flawless Welds
Blog Article
Unraveling the Secret of Porosity in Welding: Tips for Lessening Defects and Maximizing Quality
In the elaborate globe of welding, porosity continues to be a relentless challenge that can significantly impact the high quality and honesty of bonded joints. As we dive right into the midsts of porosity in welding, uncovering the tricks to its avoidance and control will be vital for experts seeking to master the art of top quality weldments.
Comprehending Porosity in Welding
Porosity in welding, a common problem come across by welders, describes the visibility of gas pockets or voids in the welded product, which can jeopardize the stability and top quality of the weld. These gas pockets are usually caught throughout the welding procedure due to different variables such as incorrect protecting gas, contaminated base materials, or inaccurate welding criteria. The development of porosity can damage the weld, making it susceptible to breaking and corrosion, ultimately causing structural failures.
By acknowledging the importance of maintaining correct gas securing, making sure the tidiness of base products, and maximizing welding setups, welders can considerably decrease the likelihood of porosity development. Generally, an extensive understanding of porosity in welding is essential for welders to generate top notch and long lasting welds.

Typical Causes of Porosity
When examining welding procedures for prospective quality problems, understanding the usual reasons of porosity is crucial for keeping weld honesty and avoiding structural failings. Porosity, defined by the visibility of tooth cavities or gaps in the weld metal, can significantly jeopardize the mechanical properties of a bonded joint.
Another common reason of porosity is the existence of dampness and contaminants externally of the base metal or filler product. When welding materials are not appropriately cleaned or are subjected to high degrees of moisture, the vaporization of these impurities during welding can produce gaps within the weld bead. In addition, welding at improper specifications, such as exceedingly high traveling speeds or currents, can produce too much turbulence in the weld pool, capturing gases and creating porosity. By dealing with these typical reasons through appropriate gas protecting, material prep work, and adherence to ideal welding criteria, welders can minimize porosity and enhance the top quality of their welds.
Techniques for Porosity Avoidance
Carrying out effective safety nets is crucial in reducing the occurrence of porosity in welding procedures. One strategy for porosity avoidance is making certain correct cleansing of the base steel prior to welding. Impurities such as oil, oil, corrosion, and paint can cause porosity, so thorough cleaning using suitable solvents or mechanical methods is important.

Utilizing premium filler materials and shielding gases that are ideal for the base metal and welding process can dramatically minimize the risk of porosity. In addition, keeping proper welding criteria, such as voltage, existing, take a trip speed, and gas flow price, is vital for porosity avoidance.
Additionally, using appropriate welding methods, such as keeping a constant traveling speed, electrode angle, and arc size, can assist stop Continue porosity (What is Porosity). Appropriate training of welders to ensure they comply with best techniques and high quality control treatments is likewise essential in lessening porosity defects in welding
Ideal Practices for High Quality Welds
One key technique is maintaining appropriate cleanliness in the welding location. Thoroughly cleaning up the work surface and bordering area prior to welding can help reduce these concerns.
Another finest technique is to very carefully choose the appropriate welding criteria for the particular products being signed up with. This includes establishing the correct voltage, present, take a trip rate, and securing gas flow rate. Appropriate criterion option makes certain optimal weld penetration, combination, and total quality. Using top notch welding consumables, such as electrodes and filler steels, can dramatically impact the final weld quality. Purchasing premium consumables why not try these out can result in stronger, much more resilient welds with fewer issues. By complying with these ideal practices, welders can consistently generate top notch welds that fulfill market standards and exceed consumer assumptions.
Significance of Porosity Control
Porosity control plays a vital function in guaranteeing the integrity and quality of welding joints. Porosity, identified by the existence of cavities or voids within the weld steel, can substantially jeopardize the mechanical residential properties and structural integrity of the weld. Too much porosity compromises the weld, making it a lot more vulnerable to cracking, deterioration, and general failing under operational tons.
Reliable porosity control is necessary for preserving the wanted mechanical homes, such as strength, ductility, helpful site and strength, of the bonded joint. What is Porosity. By lessening porosity, welders can enhance the total high quality and integrity of the weld, guaranteeing that it satisfies the efficiency requirements of the intended application
Additionally, porosity control is vital for accomplishing the desired aesthetic look of the weld. Extreme porosity not only deteriorates the weld but also interferes with its visual appeal, which can be essential in markets where aesthetics are essential. Proper porosity control strategies, such as using the proper securing gas, regulating the welding criteria, and ensuring proper tidiness of the base products, are vital for producing high-grade welds with marginal problems.
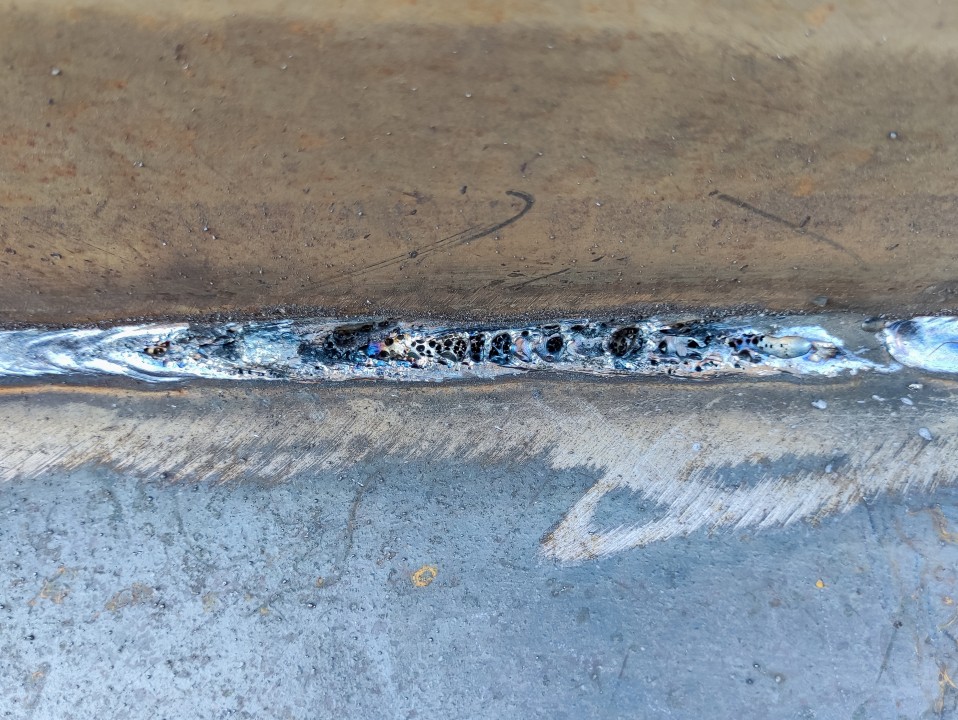

Final Thought
In conclusion, porosity in welding is a common issue that can compromise the top quality of the weld. It is important to regulate porosity in welding to make sure the integrity and stamina of the last item.
Report this page